Embedded finance has recently gone from being a ‘hot topic’ to an essential part of the global financial ecosystem.
It has game-changing and far-reaching implications for most industries.
Recent research estimates that the value of the embedded finance market, which was at $43 billion in 2021, will grow to $138 billion in 2026.
Just like the word ‘fintech‘, it means different things to different industries and companies.
So, let’s take a closer look at embedded finance and its transformative impact.

What is embedded finance?
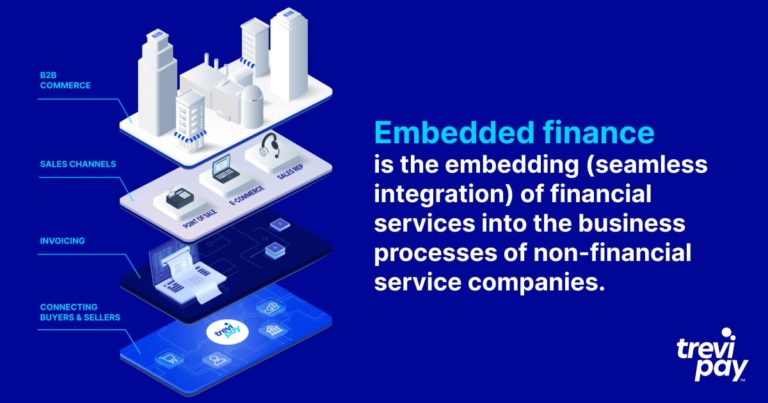
Embedded finance is the embedding (seamless integration) of financial services into the business processes of non-financial service companies.
Embedded finance includes: payment processing, lending, invoice finance, insurance, and even investing.
They are embedded via APIs (application programming interfaces) – programming code that enables different softwares to connect and integrate.
Digital wallets and embedded finance are two key concepts in fintech that enhance the consumer experience by offering integrated financial services in a seamless way.
A digital wallet (or e-wallet) is a secure virtual tool where consumers store payment information, such as credit/debit card details, bank account info, and digital currencies. This allows for quick, easy, and secure transactions both online and in-store, eliminating the need for physical cash or cards. Digital wallets are crucial for embedded finance, as they serve as the platform where consumers access a variety of financial services.
You might already be aware of the term ‘embedded payments‘. This refers to the simplification of transactions that take place within apps or other online channels so that customers can make transactions without leaving the site or app.
Uber is often cited as an example of embedded payments in a consumer scenario. Unlike a traditional taxi journey, no cash or card transaction needs to be instigated by the customer at the end of the journey. We share more examples later.
Embedded finance is the application of this same principle across a broader range of financial services such as pensions or loans, not just the payments element.
Embedded lending is a type of embedded financing that specifically refers to the integration of lending products into non-financial platforms or services. This allows consumers to access credit seamlessly within their existing user journey, often without leaving the platform they are interacting with. Embedded lending focuses exclusively on credit-based financial products, including:
- Consumer Loans: Loans for personal or consumer use, typically unsecured.
- Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL): Short-term installment loans offered at the point of purchase.
- Revolving Credit: Access to a credit line that users can borrow from, repay, and borrow again.
- Point-of-Sale Financing: Loans are provided during the checkout process on e-commerce websites or in-store.
Banking as a Service (BaaS)
When discussing embedded finance, you’ll often hear the term Banking as a Service (BaaS) mentioned.
It is the name of an outsourcing model used in embedded payments, whereby banking services are white-labeled for use by non-banking companies.
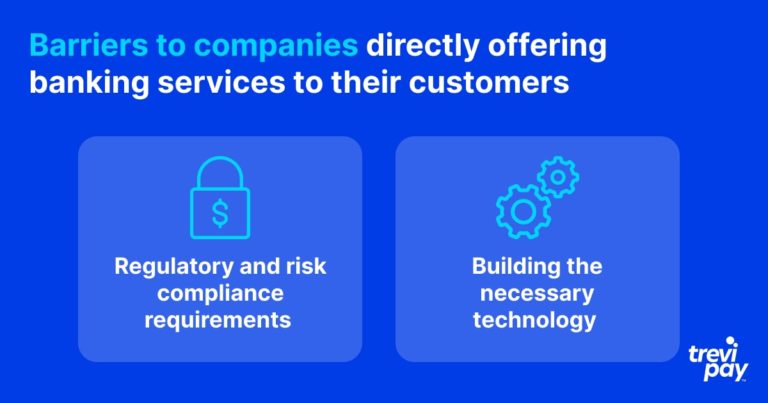
There are several barriers to companies directly offering traditional banking financial products and services to their customers, particularly:
- Regulatory and risk compliance requirements
- Building the necessary technology
BaaS providers enable companies to offer valuable services to their customers without their customers knowing that a third party is involved.
It is similar to open banking. But the difference is that the latter is when non-banking businesses provide services that only rely on using banks’ data (as opposed to their services).
Embedded Finance Examples
There are many different types of embedded finance. It is a highly varied field with innovation baked into its DNA.
The examples below give just a sample of the variety of embedded financial products available in the consumer market.

1. Klarna & buy now, pay later (BNPL): embedded lending
Klarna is a Swedish fintech company that primarily specializes in providing payment processing services for e-commerce stores. It is also well-known for its consumer buy now, pay later (BNPL) service.
BNPL is essentially a form of money lending that divides payments into installments. It makes purchases more attainable for consumers rather than paying in one lump sum using a traditional card-based method.

2. Lyft & ridesharing: embedded payments
US-based Lyft has the second biggest share of the ridesharing market in the US, after Uber.
Ridesharing (or ride-hailing) is a service that connects drivers with passengers via an app or website.
Prices are fixed (based on live local conditions) beforehand and payments are processed and recorded by the app itself. This dispels uncertainty about costs and reliance on cash, making the journey even easier than hailing a traditional cab. The passenger simply exits the cab at the end of the journey without the inconvenience and delay of finding cash or making a card payment.

3. Tesla: embedded insurance (EI)
Tesla isn’t only an innovator in electric car design and technology. Since becoming a licensed insurer, the company also offers embedded insurance (EI) in a growing number of US states.
This is very convenient for its customers who would otherwise have to pay relatively high rates from traditional insurance providers. They can simply purchase insurance at the point of sale.
Tesla’s EI provides the same cover as other insurers. What makes it unique is that its rates are calculated using live data from the vehicle owner.
The benefits of embedded finance
There are multiple benefits of embedded finance both in the context of B2B and consumer scenarios. These will vary according to the precise method, but the benefits listed below generally apply across all iterations of B2B and consumer-embedded payments.

1. Increased revenue
The primary benefit of embedded finance is that it makes customer spending easier and, therefore, promotes increased sales and revenue growth.
2. Increased convenience
Embedded payments make transactions effortless and time-saving.
This is most evident from a customer experience point of view. Nowadays, even the simple task of having to re-enter bank account details repeatedly is seen as an inconvenience that can cause a purchase to be abandoned.
The B2B customer experience has recently begun to see a similar level of attention as the consumer experience. Providing a frictionless B2B process is an opportunity for businesses not only to grow revenue but also to differentiate themselves in the market.
For businesses without a BaaS provider, the time, effort, and risk of developing and maintaining a native version of the same service would be too much of a barrier. Qualifying for regulatory certification alone would be both excessively expensive and time-consuming.
3. Increased customer sign-up and loyalty
The prestige and trust that comes with offering innovative financial services is hugely beneficial from a repetitional and brand standpoint.
Also, loyalty is hugely important to companies offering both B2B and consumer services. Embedded finance and especially embedded payments can make a difference here by enhancing customer experience. For example, offering a line of credit that can be spent easily online is likely to keep B2B customer coming back.
By neglecting to adopt an embedded finance or embedded payments strategy, companies risk losing business to more forward-thinking competitors.
4. Improved analytics
Embedded finance enables improved data collection and analytics.
The nature of the technology involved means real-time updates and detailed reporting are often available.
The right system will also simplify the consumer feedback process. This can help companies understand their customers’ pain points better, implement more impactful marketing and inform their future development.

Traditional financial institutions vs alternative lenders
Despite their name, BaaS services aren’t necessarily provided by banks. In fact, many are provided by fintechs and other non-bank companies.
Banking is a very old business model and many current banks still have deep roots in the past. Some have made steps towards digital reinvention – influenced in part, no doubt, by the challenge posed by fintechs.
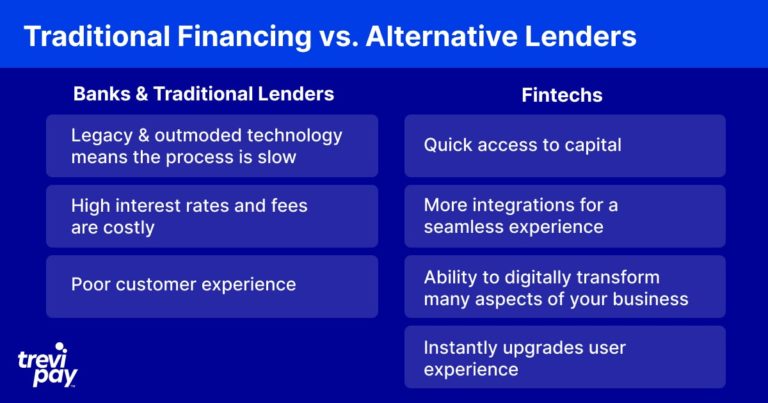
However, legacy banks still primarily make money through traditional loans and are underpinned by outmoded technology. This means that their operations are often slow and customer experience is poor.
Fintechs are designed around modern technology and cutting-edge specialist tools. This allows them to connect with other data sources, process information more quickly and offer a much better user experience to customers.
Using new technology also means fintechs don’t have to maintain large and complex IT systems so they can usually be relied on for more competitive pricing than incumbent providers of financial services.
Embedded finance for B2B: How TreviPay Can Help
Whilst there are many examples of embedded finance for the consumer market, as mentioned above, it is also increasingly an essential part of business-to-business (B2B) propositions.
These are growing in popularity as businesses acknowledge that the expectations of B2B buyers are rising quickly based on their experiences as consumers.
B2B financing itself is a fast-growing and innovative field. The kinds of solutions most frequently used in B2B and their scale obviously differ from B2C.
For example, invoice financing is a popular way for businesses to efficiently leverage their existing accounts to improve cashflow.
At TreviPay, we specialize in providing effective embedded B2B financing solutions, from different types of invoice financing to payment and Net 30 terms. Partner with us to streamline your B2B financing needs and stay ahead in the competitive market. Explore our solutions to see how we can help your business grow efficiently and securely.